Financial leverage is a fundamental concept in finance that plays a crucial role in both corporate finance and investing. It refers to the use of borrowed funds to increase the potential return on investment. In this blog, we will explore what financial leverage is, how it works, and its advantages and risks.
What is Financial Leverage?
Financial leverage involves using debt (borrowed money) to finance the acquisition of assets. The idea is that by using debt, a company or investor can acquire more assets than they could with their own capital alone. This can amplify both potential gains and potential losses.
How Financial Leverage Works
To understand how financial leverage works, consider a simple example:
- Without Leverage: Suppose an investor has $100,000 to invest in a stock. If the stock’s value increases by 10%, the investor’s portfolio value rises to $110,000, yielding a $10,000 profit.
- With Leverage: If the same investor borrows an additional $100,000 and invests a total of $200,000 in the stock, a 10% increase in the stock’s value will result in the portfolio value rising to $220,000. After repaying the $100,000 loan, the investor is left with $120,000, yielding a $20,000 profit.
In the leveraged scenario, the investor’s return is doubled, illustrating the amplifying effect of leverage.
Advantages of Financial Leverage
1. Increased Returns
As demonstrated in the example, financial leverage can significantly increase the potential return on investment. This is particularly attractive in bullish markets where asset values are rising.
2. Tax Benefits
Interest payments on borrowed funds are often tax-deductible, reducing the overall cost of borrowing and effectively lowering the tax burden on the borrower.
3. Capital Efficiency
By using debt, companies and investors can make more efficient use of their capital. This allows them to undertake larger projects or investments than would be possible with their own funds alone.
Risks of Financial Leverage
1. Increased Losses
While leverage can amplify gains, it can also amplify losses. If the value of the investment falls, the losses will be magnified, and the borrower will still need to repay the borrowed amount.
2. Interest Costs
Borrowing money incurs interest costs. If the return on the leveraged investment does not exceed the cost of borrowing, the financial leverage can result in a net loss.
3. Bankruptcy Risk
High levels of leverage increase the risk of bankruptcy, especially if the borrower is unable to meet interest payments. This is particularly risky for companies with unstable cash flows.
Measuring Financial Leverage
Financial leverage is commonly measured using ratios such as:
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio: This ratio compares the company’s total debt to its shareholders’ equity. A higher ratio indicates more leverage.
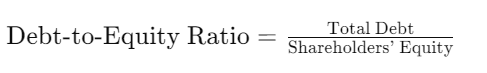
- Interest Coverage Ratio: This ratio measures a company’s ability to pay interest on its debt from its operating income. A lower ratio indicates higher risk.
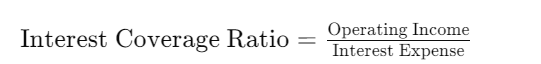
Conclusion
Financial leverage is a powerful tool that can enhance returns on investment by using borrowed funds. However, it comes with significant risks, including the potential for amplified losses and increased bankruptcy risk. Investors and companies must carefully consider these factors when deciding to use leverage. By understanding the dynamics of financial leverage, investors can make more informed decisions and better manage the associated risks.

2 thoughts on “What is financial leverage in financial Market ?”